Review Oncomine™ cfDNA assay run results
The Completed Runs Report from an Oncomine™ cfDNA Assay run is similar to variantCaller plugin reports. The following outputs have been added.
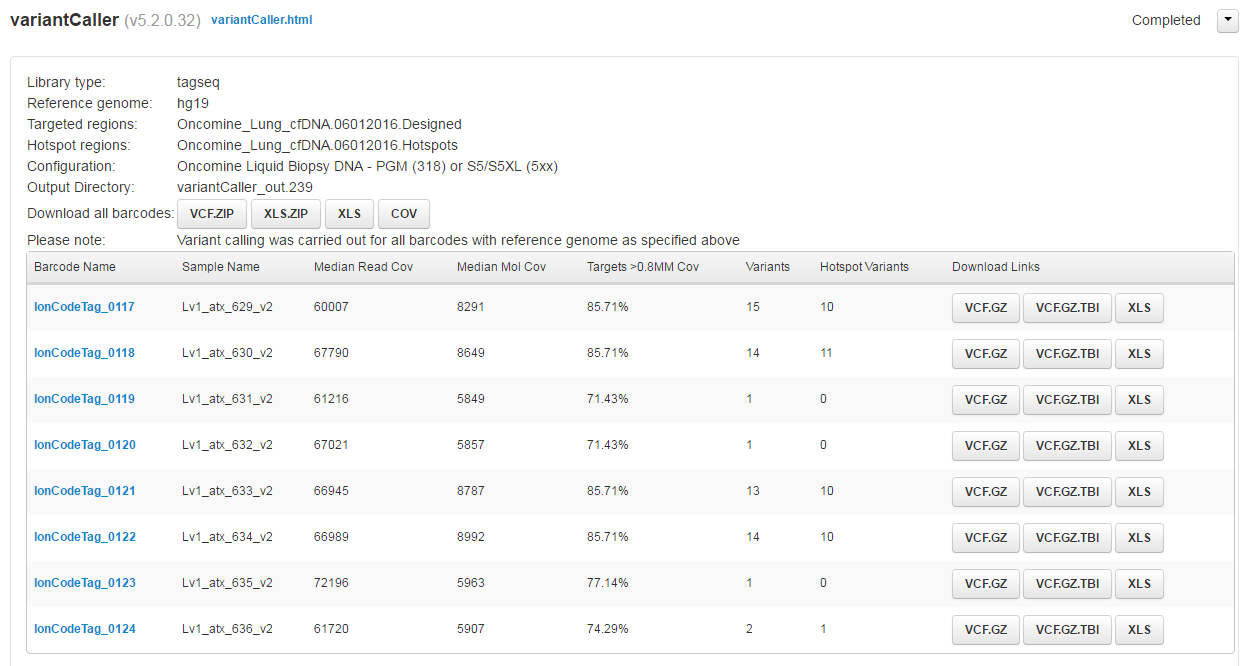
- After the run is complete, in the Data tab, click Completed Runs & Reports, then click the Run Report for your results.
- To view a summary of the variant analysis, scroll down to the variantCaller section, then click the appropriate button to download variant calls in .vcf or .xls formats.
-
Review the results in the Median Read Cov, Median Mol Cov, and Targets >0.8MM columns.
Column
Description
Median Read Coverage
Reports median coverage across targets. Median Molecular Coverage reports median number of individual interrogated DNA molecules across targets.
Targets >0.8 Median Molecular Coverage
Reports percent of targets with molecular coverage within 80% of the median coverage value. This is a new stricter definition of panel uniformity.
Median Read Coverage and Targets >0.8 Median Molecular Coverage
Measures the quality of the sequencing run and library performance, while Median Molecular Coverage measures the amount and quality of the input DNA sample.
Median Molecular Coverage
Directly influences the limit of detection in a sample run. We always require two independent molecular families to identify a variant for it to be called. Lower median molecular coverage values result in less sensitive detection of variants at 0.1% frequency, although still sufficient for sensitive detection of variants with higher frequency. For example, Median Molecular Coverage of 700 is sufficient for accurate detection of variants at 0.5% frequency.
For sensitive variant detection down to 0.1% frequency, we see optimal results when targeting a Median Read Coverage >25,000, Median Molecular Coverage >2,500, and Targets >0.8 Median Molecular Coverage >60%.
-
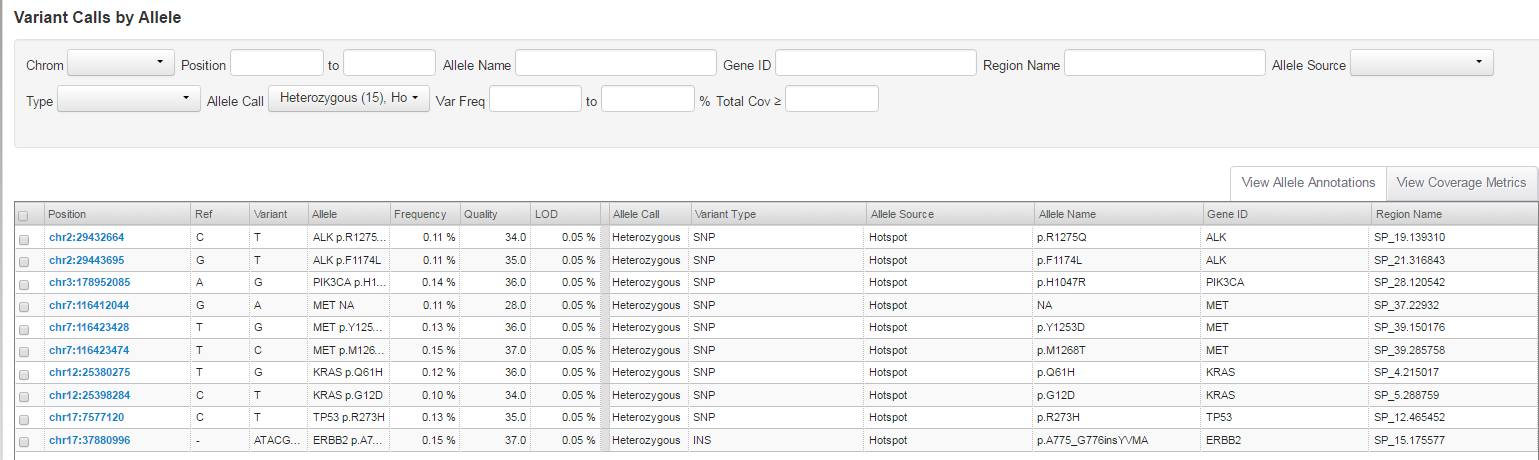
Click a Barcode Name of interest to review Variant Calls by Allele.
By default only hotspot alleles calls are shown in the variant table. We do not report hotspot alleles that did not meet our criteria for calling. However, we do provide at least one record for each hotspot position. This can include: novel allele call at hotspot position, hotspot allele call, or absent call when the first two are missing.
Column
Description
Frequency
Reports the observed frequency of hotspot allele.
LOD
Reports limit of detection at hotspot position, which is based on the number of interrogated DNA molecules (fragments) containing target.
We use the term 0.1% LOD to mean we have data to support specific sensitivity and specificity claims (90% and 98%) at the 0.1% allelic frequency. By default, our analysis tool uses minimum alternative allele frequency threshold of 0.05% and we have a technical lower limit of detection of 0.03% for this method.
Observed frequency can be lower than LOD due to sampling nature of the assay.
If selected to display hotspot positions with absent variant call, then only one record per hotspot position is displayed and only one of the hotspot alleles at that position is displayed under "Allele Name".
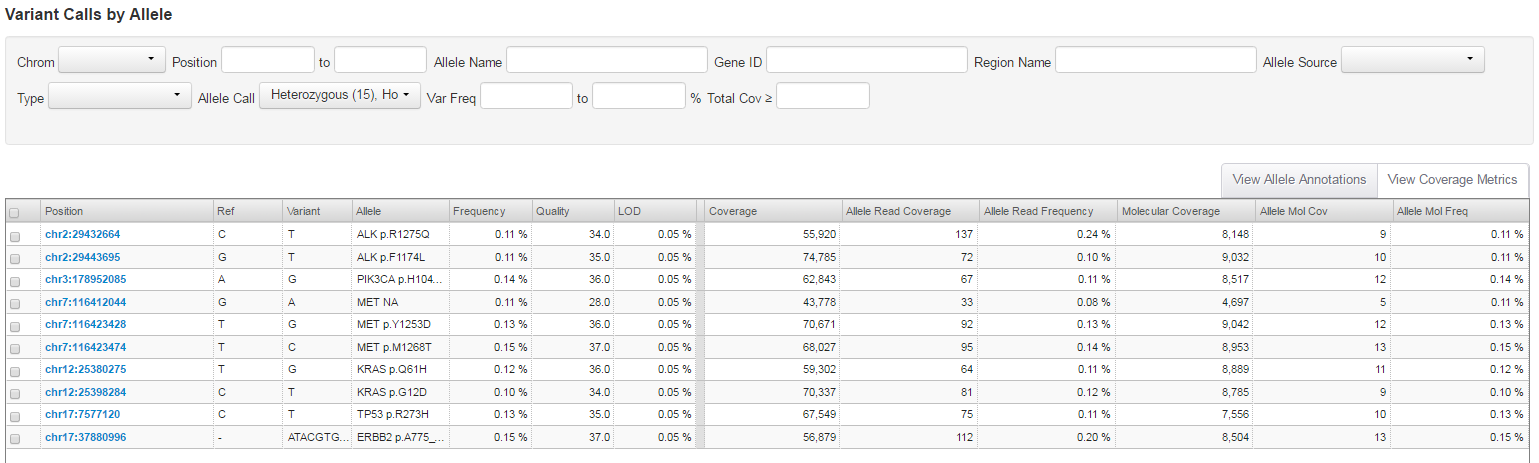
- Click View Coverage Metrics to view the total number of interrogated DNA molecules at hotspot positions (Molecular Coverage), and the number of molecules containing the variant (Allele Mol Cov).
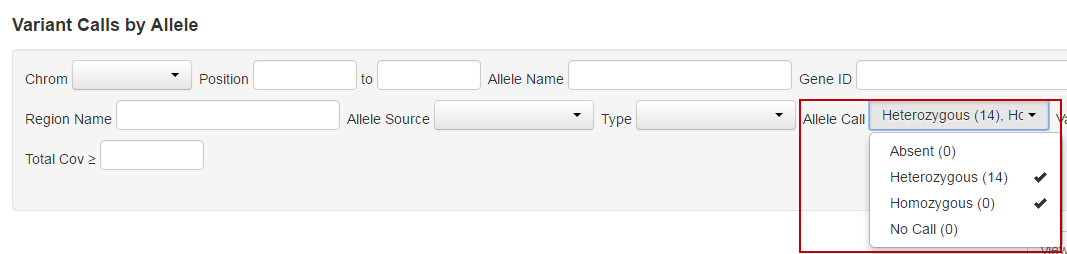
- You can modify the types of calls that are displayed in the Allele Calls dropdown list, by selecting or deselecting Absent, Heterozygous, Homozygous, or No Call. No calls are variant calls that are classified as systematic errors.
- Select Absent in the Allele Call dropdown list to visualize hotspot positions without a valid variant call that meets our analysis criteria. We report one record per hotspot position with missing alternative call, and the alternative allele is an arbitrary value distinct from reference. LOD and molecular coverage metrics at those positions are measurements for variant absence among many interrogated molecules.
- To view novel alleles, select Novel (sequenced allele that is different from the expected allele defined in the panel hotspot file) in the Allele Source dropdown list.